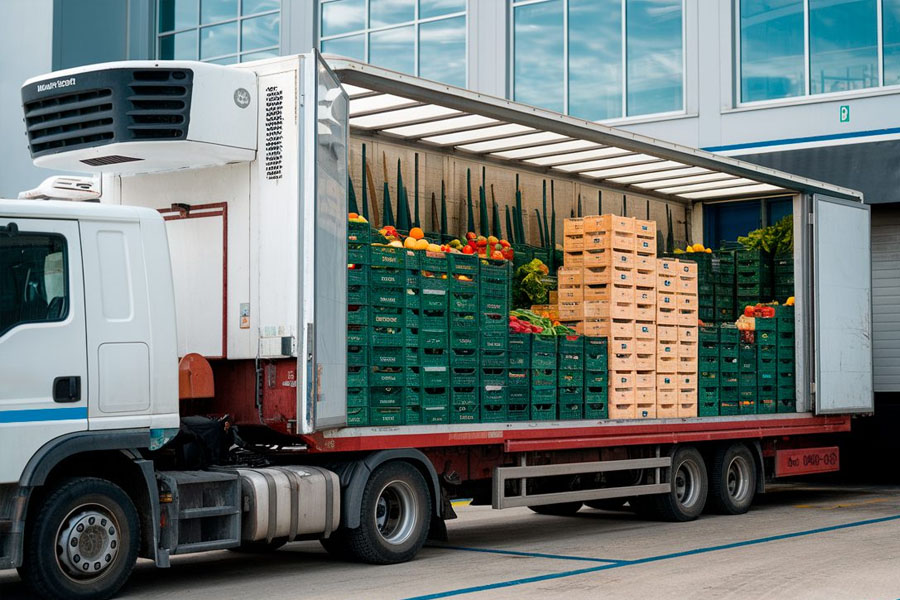
Why Cold Chain Logistics Matter
Temperature-sensitive goods live on a tightrope. A few degrees off and quality slips, safety suffers, and value can vanish. Refrigerated transport sits at the center of this balancing act. It carries fresh food, pharmaceuticals, and specialty materials from dock to door while protecting them from heat, contamination, and delay. These vehicles are more than delivery trucks. They are controlled environments on wheels, tuned to sustain the precise conditions products need to arrive ready for shelves, labs, and kitchens.
Temperature Control From First Mile to Last
The promise of cold chain operations is temperature control. Even as weather, traffic, and route profiles change, modern chilled fleets maintain internal conditions with insulated cargo bays, powerful refrigeration units, and calibrated sensors. Cold air is managed to reach every nook. Careful construction eliminates thermal bridging. Door seals tightly. Every feature avoids hot spots and rapid adjustments.
Even small deviations can be costly. Leafy greens wilt. Dairy separates. Biologics degrade. By holding narrow set points from loading dock to final delivery, refrigerated vehicles preserve product integrity and maintain safety. Drivers and dispatchers monitor readings continuously. Alerts help them respond fast if temperatures start to drift. The vehicle becomes a moving thermostat, actively guarding the goods within.
Hygienic Design That Stops Contamination
Cleanliness is a second pillar of cold chain success. Interior surfaces are smooth, nonporous, and easy to sanitize. Corners are rounded to prevent debris buildup. Drainage points are accessible for thorough cleaning. Racks and tie-downs are arranged to reduce clutter and eliminate places where residue can hide.
Hygiene protocols set the rhythm of daily operations. Crews follow cleaning schedules that include disinfecting walls, floors, and equipment. Tools are dedicated to chilled environments and stored properly to avoid cross-contact. Waste is removed quickly. The habits seem simple but they matter. When sanitation is consistent, the risk of contamination drops and products remain fit for consumption or use.
Intelligent Cooling Systems and Real-Time Sensing
Refrigeration units in transport vehicles are built for precision. They do more than chill air. They vary compressor speeds to match load requirements. They modulate fans to balance airflow across the cargo space. They work with thermal insulation to keep energy demand reasonable, all while holding target temperatures within tight tolerances.
Sensors serve as the eyes and ears of this operation. Thermocouples, infrared probes, and humidity monitors feed data to a central controller. If cargo doors open, systems adjust quickly. If external temperatures spike, capacity ramps up. This intelligence helps maintain the delicate equilibrium that sensitive goods require. Pharmaceuticals need stable thermal ranges so compounds remain active. Fresh proteins rely on continuous cold to keep bacteria from proliferating. With data flowing in, the vehicle reacts before conditions drift far enough to cause spoilage.
Skilled Handling That Protects Quality
Equipment cannot compensate for poor loading. Skilled handling ensures cold air can circulate, products are supported, and packages stay undamaged. Staff trained in cold chain procedures pre-cool cargo areas. They stage goods so the time between warehouse and vehicle is minimal. They group items by temperature requirement and stack in patterns that prevent crushed boxes and blocked vents.
Door discipline is part of the craft. Teams plan their steps to avoid frequent openings and prolonged exposure. If multiple drops are scheduled, the load is arranged so quick access reduces warm air intrusion. Pallets are secured to prevent shifts that restrict airflow. Every movement is intentional. The result is steady temperature, reduced mechanical stress on items, and a lower chance of cross-contamination.
Compliance With Standards and Traceability
Cold chain logistics operate under strict rules designed to protect consumers. Requirements cover temperature accuracy, sanitation, record keeping, calibration, and training. Providers maintain documentation for each shipment. Data logs capture temperature and humidity across the journey. Sensors are calibrated on schedule and records are kept for audits. Cleaning checklists are signed and stored. Drivers receive recurring training on food safety and handling, or on Good Distribution Practices for medical products.
Rules change, so procedures must too. Fleets are inspected inside to ensure equipment and interior hygiene. Supplier-to-recipient traceability. If problems emerge, records show when conditions changed. Compliance eliminates legal risk and develops client trust in confirmed quality.
Smart Routing That Preserves Freshness
Time is an ingredient in product quality. Route planning trims waste and keeps conditions stable. Dispatchers analyze traffic patterns, delivery windows, vehicle capacity, and customer time constraints. They schedule the sequence of stops to minimize door openings and prevent unnecessary detours. If certain goods must arrive at specific temperatures, they get first position on the route. If a region is prone to congestion, departure is adjusted to avoid the worst hours.
Efficient routing saves fuel. It also prevents thermal swings that come from extended idling or unexpected delays. For clients, this means reliable arrival times and consistent product quality. For providers, it means healthier margins and fewer exceptions to manage.
Preventive Maintenance That Keeps Fleets Ready
Mechanical reliability maintains cold chain performance. Refrigerators and engines undergo scheduled maintenance. Technicians inspect belts, compressors, fans, seals, and electrical connections. They check insulation, door gaskets, drains, and condensate lines. Control systems and temperature probes are calibrated. Maintaining tires, brakes, and suspension stabilizes the ride and protects cargo.
Scheduled maintenance reduces breakdowns and on-route malfunctions that could threaten cargo. With vehicles designed for heavy workloads and frequent stops, consistent service keeps them ready for demanding routes. When fleets are reliable, the chain stays intact and perishable goods arrive in the condition customers expect.
Integrated Performance Across the Cold Chain
Cold chain success is a synchronized act. Temperature management, hygiene, smart cooling, trained handling, regulatory compliance, efficient routing, and preventive maintenance all reinforce one another. Each element contributes to the integrity of the product throughout the journey. When providers prioritize these pieces and bind them together with clear procedures and attentive teams, businesses gain a dependable channel. Perishables retain their qualities. Safety is protected. Value holds.
FAQ
What products typically require refrigerated transport?
Goods that are sensitive to heat or microbial growth travel with refrigeration. These include fresh produce, dairy, meat, seafood, frozen food, ready-to-eat meals, vaccines, biologics, specialty chemicals, and certain cosmetics. Some items need very narrow ranges while others are flexible, but all depend on stable temperatures and clean handling.
How are temperatures monitored during transit?
Vehicles use calibrated sensors placed at strategic points inside the cargo area. Readings feed into onboard controllers and telematics systems that display values to drivers and dispatchers. If temperatures drift toward limits, alerts prompt immediate action. Data logs are captured for the full journey to support traceability and compliance.
What happens if a refrigerated truck experiences a breakdown?
Contingency plans guide the response. Drivers notify dispatch, and support teams assess whether repairs can be performed on site or if a substitute vehicle should be sent. Cargo doors remain closed to conserve cold air. If necessary, goods are transferred quickly to a working unit that has been pre-cooled. Documentation notes the event, and temperature logs confirm product integrity.
Can these vehicles control humidity as well as temperature?
Many refrigerated systems manage humidity indirectly through airflow patterns and cooling cycles. Some setups include dedicated humidity control for products that need tighter moisture ranges, such as certain pharmaceuticals or produce. Proper packaging also helps stabilize humidity around the goods.
How do handlers keep the cargo area hygienic between deliveries?
Crews follow cleaning schedules that pair routine disinfecting with deeper sanitation at defined intervals. Surfaces are washed and sanitized, drains are cleared, and equipment is wiped down. Waste and residue are removed promptly. Tools used in the cargo area are cleaned and stored to avoid cross-contact. Records confirm when and how cleaning was performed.
Which regulations shape cold chain operations?
Standards cover temperature accuracy, sanitation practices, training, calibration, and record keeping. Providers maintain logs for each shipment, train staff on handling protocols, and calibrate sensors regularly. Vehicles and facilities are inspected to confirm compliance. These measures protect end users and provide assurance that products were maintained within required conditions throughout transit.